Historical aspect
The YaMZ 236 motor was developed in 1951 on the basis of the YaAZ 204 and YaAZ 206 power units. The production of these internal combustion engines was carried out by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant, which later became Avtodizel OJSC.
Assembly shop of the Yaroslavl Motor Plant.
During the installation and modernization process, YaMZ engines began to be permanently installed on MAZ, URAL, KRAZ trucks, K-700 tractors and some military equipment, especially tanks and all-terrain vehicles.
Yaroslavl diesels, hope, support and torque
Perhaps the only enterprise that is capable of producing competitive diesel engines for trucks and construction equipment remains the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. YaMZ diesel engines are brutal, reliable, simple and unpretentious, sometimes even showing miracles of integration into the new century with its stringent requirements for environmentally friendly exhaust. Thus, all diesel engines that are installed today on Ural, MAZ, Ivanovo and Kostroma excavators comply with at least Euro 0 standards.
In particular, today we will be interested in the six-cylinder naturally aspirated diesel engine YaMZ 236, installed on a huge number of road and construction equipment, MAZ, Ural vehicles, diesel generators and some buses. The motor was developed 55 years ago, but due to the lack of an alternative, it continues to be in demand. By modern standards, even for a diesel unit of the most utilitarian construction equipment, it simply has no equal. In the sense that there is hardly any other manufacturer in the world that sells working museum exhibits. However, the 180 horsepower extracted from the 11.2-liter V-6 cylinder engine is put to good use.
Video about the YaMZ-236 engine
The basic YaMZ 236 engine can be equipped with many improvements and attachments:
- power take-off mechanism;
- mechanism for damping torsional vibrations;
- oil-liquid radiator,
and some other devices associated with the narrow specialization of certain equipment. There is also a modification of the YaMZ 236 HE2 Turbo engine. It is equipped with a turbocharger and as a result, the power increased to 230 forces. The price of the engine, by the way, without gearbox and clutch is 460,000 rubles.
But no matter what attachments are installed on this diesel engine, maintenance and adjustments are simply inevitable. The motor is easy both to set up and to maintain, since you still need to know how to damage it. Still, some technological processes require explanation, in particular, adjustment of the valve mechanism.
Technical characteristics and device
The technical characteristics of the YaMZ 236 engine have not changed much since the start of engine production. Only some technical and design elements have been added, such as turbocharging, power supply or exhaust gas systems.
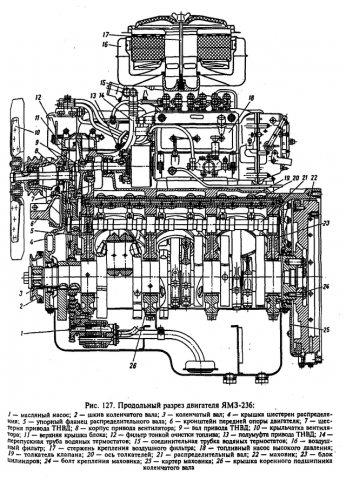
Technical characteristics of the YaMZ 236 motor.
The main technical characteristics of the internal combustion engine 236 YaMZ.
| Name | Characteristic |
| Type | Diesel, turbocharged diesel |
| Volume | 11 liters (11,150 cm3) |
| Configuration, parameter | V-shaped |
| Number of cylinders | 6 |
| Number of valves | 12 |
| Econorm | from Euro-0 to Euro-4 |
| Cylinder diameter | 130 mm |
| Compression ratio | 17,5 |
| Cooling | Liquid |
| Valve mechanism | OHV |
| Material of block and head | Cast iron |
| Resource | 800,000 - 1,000,000 km |
| Fuel | Diesel fuel |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-4-2-5-3-6 |
| Applicability | MAZ, KRAZ, URAL, T series tanks, K tractors, LAZ buses, CHETRA all-terrain vehicle and more |
Motor modifications
At different times, there were different modifications of engines manufactured by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. So, what types can be found on cars:
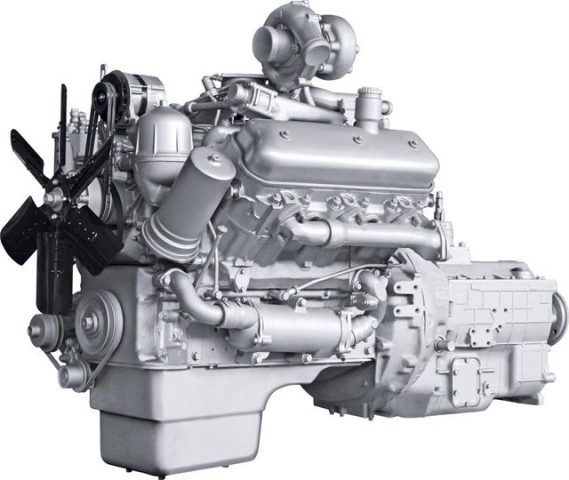
Engine YaMZ 236.
- YaMZ-236G - 150 hp. (110 kW) at 1700 rpm.
- YaMZ-236DK - 175 hp. (129 kW) at 2100 rpm, 667 N•m (68 kgf•m) at 1400 rpm.
- YaMZ-236ND - 210 hp. (154 kW) at 1900 rpm, 882 N•m (90 kgf•m) at 1300 rpm.
- YaMZ-236N - 230 hp. (169 kW) at 2100 rpm, 882 N•m (90 kgf•m) at 1300 rpm.
- YaMZ-236BK - 250 hp. (184 kW) at 2000 rpm, 1030 N•m (105 kgf•m) at 1200 rpm.
- YaMZ-236B - 250 hp. (184 kW) at 2000 rpm, 1030 N•m (105 kgf•m) at 1300 rpm.
- YaMZ-236BE2 - 250 hp. (184 kW) at 2000 rpm, 1078 N•m (110 kgf•m) at 1200 rpm.
- YaMZ-7601 - 300 hp. (220 kW) at 1900 rpm, 1275 N•m (130 kgf•m) at 1200 rpm.
Applicability
YaMZ 236 engines have become quite widely used. Thus, about two dozen brands and more than 40 models of cars, buses, military vehicles and construction equipment are still equipped with legendary engines.

URAL with YaMZ 236 engine.
The URAL-4320 with the YaMZ 236 engine has become quite popular. In addition to this brand of engine, there is also an older brother - the YaMZ-238. This motor is much more powerful, and therefore is installed on heavy construction equipment, tractors, and even strategic military vehicles.
Why have YaMZ engines become widespread? Unlike their Western counterparts, domestically produced power units are quite easy to repair and do not have a large amount of electronics, which makes repairs possible in the field.
Also, the motors have the necessary power so that the vehicle can pull a load even in the most difficult conditions. For example, sand that gets into the fuel system is not a hindrance, and it is easily removed from the engine.
So, let's look at which vehicles the YaMZ-236 power unit can be found on:
- The first in line, of course, are MAZ cars. The engines can be found on such models as: 500, 503, 504, 509, 516, 5335, 5549, 5551 and others.
- The second most widely used vehicle is the KRAZ: 255, 250, 257, 260 and 6322.
- Also installed on URAL series vehicles: 4320, URAL 5323.
- Also, the YaMZ-236 engine was also used on KAMAZ. So, the model 5320 was equipped from 1976 and 2000.
Adjusting valves Yamz 236
Adjusting the Yamz 236 valves is difficult for only one reason. This engine does not have a TDC piston position lock. Therefore, it is necessary to look for this position at the time of injection on the first cylinder. I’ll tell you right away the adjustment schemes, with cranking the crankshaft in one revolution, I immediately rule out. Very high probability of error. And then you simply have to adjust the valves again. This method requires a perfectly precise position of the piston at TDC. Which is very difficult to achieve on such engines.
Adjustment on the Yamz 236 engine has a number of features that you need to know well.
Firstly, the engine is six-cylinder. You need to know the operating order of the cylinders. He is such a
operating procedure of Yamz 236 cylinders
1-4-2-5-3-6
Knowing the operating procedure, it is necessary to find the position of the piston of the first cylinder at the moment of compression. I repeat that there is no lock on this engine, and looking for marks on the front pulley and flywheel is very inconvenient. Therefore, it can be easier to determine by the position of the valves of the first cylinder.
Secondly . The size of the thermal clearances for the intake and exhaust valves is the same.
When adjusting, you always ask yourself these questions. This is how to say the main points that there is no need to doubt. If you haven’t adjusted the valves on this particular model for a long time.
Where to begin.
The engine must be cold, because the permissible clearances are provided specifically for a cold engine.
It is necessary to remove the valve covers and determine which valves are inlet and which are exhaust. This is not difficult to do, because the exhaust valves are located opposite the exhaust manifold channels, and the intake valves are located opposite the intake manifold channels. You can also navigate by the direction of the engine. In the right lane in the direction of travel, the exhaust valves are located towards the cooling fan. And in the left row, the exhaust valves are located towards the flywheel.
Adjusting valves YaMZ 236
We start the adjustment from the first cylinder. It is located on the right side in the direction of travel of the car. Now it is very important to determine the position of the top dead center (TDC) of the first cylinder at the moment of compression of the fuel mixture. In this position, the inlet and outlet valves should be closed.
Rotate the crankshaft clockwise (looking at the front end of the engine) until the intake valve is completely closed. That is, the intake valve rocker arm should rise up and remain motionless during further rotation. We continue to rotate the crankshaft until the exhaust valve closes. As soon as it closes, stop rotating. This will be the position of the piston at TDC at the moment of compression.
It is very important not to make a mistake here; it is from this position that the remaining valves will be adjusted. It's better to check yourself again. In this position, the ignition timing marks will be close to their alignment. The ideal option is if they are combined, but in this case such precision is not needed. The exhaust valve has closed and that's enough.
To adjust the valve of the first cylinder. A 0.25mm feeler gauge should fit between the valve and rocker arm with little effort, but if you use a 0.30mm feeler gauge, it should experience some resistance.
After adjusting the valves of the first cylinder, we move to the other side and begin adjusting the fourth cylinder. We continue to rotate the crankshaft in the same direction. And I repeat once again, we wait until the intake valve closes and with further rotation the exhaust valve closes, at the moment of complete closing we begin adjusting the valves of cylinder 4, then in the same order we sequentially adjust cylinders 2, 5, 3, and 6.
Cylinder layout on the engine
I repeat. There is a scheme for adjusting the valves per revolution of the crankshaft. Because you set the crankshaft in one position and adjust the valves according to the diagram. Then you turn the crankshaft one turn and adjust the remaining valves according to the diagram. I have never used this and do not recommend it to anyone. There is a very high probability of error in the accuracy of the crankshaft position. As a result, you spend more time and effort adjusting the valves. Because everything has to be redone
It is very important to make timely adjustments. Increased clearances will lead to late opening and early closing of valves. Which will affect the power characteristics of the engine, and as a result, fuel consumption will increase. And the absence of thermal gaps will not allow the valve to close completely, as a result the valve will burn out. Adjusting the YaMZ 236 valves does not take too much time, access to the valves is convenient, and you need to be especially careful with it.
Service
Maintenance of the YaMZ 236 engine is identical, as for all identical domestically produced diesel engines. Thus, service intervals are carried out every 15,000 km for the basic version, and for a turbodiesel - every 20,000 km.
The maintenance process is slightly different from regular gasoline engines. Each maintenance is a whole complex of operations aimed at maintaining the technical condition of the car. What is included in the maintenance of YaMZ 236 series engines:

T-150 with YaMZ 236 engine.
- Change of oil.
- Valve Mechanism Adjustment
- Replacing filters. So, depending on the engine modification, the following filter elements may or may not be present: a fine and coarse oil filter, a filter element for coarse and fine fuel purification, an air filter, an eco-filter for exhaust.
- Cleaning the injectors.
- Adjustments related to the high pressure fuel pump.
- Other operations aimed at maintaining the power unit.
The YaMZ 236BE2 engine is a four-stroke, 6-cylinder, V-shaped cylinder arrangement, displacement 11,150 cm3, liquid cooling, direct fuel injection, liquid-oil heat exchanger, mechanical speed controller, intermediate cooling of charge air in an air-to-air heat exchanger. air” installed on the car, turbocharging, complies with environmental standards for the emission of harmful substances UNECE No. 49-02B, No. 24-03-Euro-2, No. 96-01. The YaMZ 236BE2 engine can be equipped with a gearbox and clutch and has a service life of 800,000 km before major overhaul.
Main technical characteristics of YaMZ-236BE2 and its modifications
| Characteristics | Meaning |
| Power, kW (hp) | 184 (250) |
| Rotation speed, rpm | 2000 |
| Maximum torque, N.m (kgf.m) | 1078 (110) |
| Frequency at maximum torque rpm | 1100-1300 |
| Minimum specific fuel consumption, g/kWh (g/l.h.) | 197 (145) |
| Overall dimensions, mm (length/width/height) | 2180/1045/1070 |
| Weight, kg | 985 |
| Clutch | YaMZ-182 |
| Transmission | YaMZ-238VM7 |
| injection pump | 135.5-10 |
| Generator | 1322.3771 |
The YaMZ 236BE2 engine has the following operating modifications YaMZ 236BE2-2, -236BE2-6, -236BE2-11, -236BE2-14, -236BE2-16, -236BE2-19, -236BE2-21, -236BE2-22, -236BE2- 23, -236BE2-24. All these engines have similar technical characteristics to those indicated in the table for the YaMZ 236BE2 and differ only in dimensions, weight, sometimes clutch, gearbox and generator model. The main structural differences are discussed below.
The YaMZ 236BE2 engine has some notable design differences: it is assembled on the basis of the YaMZ-236NE2 and has individual cylinder heads.
YaMZ 236BE2-2 has the following structural differences: it is assembled on the basis of the YaMZ 236BE2-1, does not have a starter, but has an installed lower mounting bracket, is equipped with a YaMZ-182 clutch and a YaMZ-238VM7 gearbox, has dimensions of 1275/1045,1070 mm (d/ w/h) and a weight of 980 kg, is used on MAZ-522603, -630303, -543203, -543403, -551603 vehicles and is supplied as spare parts.
YaMZ 236BE2-6 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of YaMZ 236NE2-1, has a sealed starter, generator 6582.3701-03, fan clutch, fan impeller with a diameter of 660 mm, oil sump mounted with the deep part forward, no crankshaft pulley, no equipped with a clutch and gearbox, has dimensions equal to 1300/1045/1140 mm and a weight of 985 kg, used on the MZKT-8022 chassis.
The YaMZ 236BE2-11 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of the YaMZ 236BE2-2, equipped with a YaMZ-182 clutch, a YaMZ-238VM1 gearbox with an end-mounted power take-off, has dimensions of 1275/1045/1070 mm and a weight of 980 kg, used on the MAZ-533603 chassis -240, -630303-245, supplied as spare parts.
YaMZ 236BE2-14 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of YaMZ 236NE2-3, equipped with a fan clutch, generator 6582.3701-03, flywheel housing, starter, sealed clutch housing, liquid metal coolant supplied by MAZ, YaMZ-183-10 clutch, gearbox YaMZ-336-04, has dimensions 1840/1045/1070 mm and weight 1025 kg. This modification is used on Ural-430-41 vehicles with a ford of 1.7 m.
YaMZ 236BE2-16 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of YaMZ 236BE2-1, has a front support (7511), oil level indicator, generator 6582.3701-03, fan clutch, YaMZ-182 clutch, YaMZ-2384 gearbox, has overall dimensions dimensions 2498/1045/1140 mm and weight 1470 kg, used on BZTK-8027 crane chassis.
The YaMZ 236BE2-19 has the following structural differences: it is assembled on the basis of the YaMZ 236BE2-6, equipped with a YaMZ-182 clutch, a YaMZ-238VM7 gearbox, has a mass of 1385 kg and dimensions of 2180/1045/1140 mm, and is used on the MZKT-8022-020 chassis.
YaMZ 236BE2-21 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of YaMZ 236BE2-11, equipped with a YaMZ-182-10 clutch, a YaMZ-2381-02 gearbox with a creeper, has a mass of 1385 kg and dimensions 2180/1045/1070, mounted on a MAZ chassis -53363-240, -630303-245 and used as spare parts.
YaMZ 236BE2-22 has the following structural differences: assembled on the basis of YaMZ 236BE2-2, equipped with a YaMZ-182-10 clutch, a YaMZ-2381-02 gearbox with a creeper, has a mass of 1385 kg and dimensions 2180/1045/1070, installed on on-board vehicles , chassis, truck tractors, dump trucks MAZ-533603, -630303, -543203, -543403, -551603 and their modifications.
YaMZ 236BE2-23 and YaMZ 236BE2-24 have the same parameters and a very similar design, they are used on cars, chassis, KrAZ-6510, -65101, -65053, -65055 dump trucks.
Repair
Repair of the YaMZ 236 engine is carried out quite standardly for the entire series of engines produced by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. Thus, in-line repair work is carried out directly on the car.
Depending on the make, model and design features of the vehicle on which the engine is installed, even major repairs can be performed without removing the power unit. Moreover, this is a condition that no boring is required.

The process of overhaul of YaMZ 236.
Often, if a restoration or major overhaul is underway, the engine is bored. As recent practice shows, most old cylinder blocks are not subject to boring and honing, and therefore they undergo a liner process. The block heads are quite durable, which makes it possible to go through them not often, but when overhauling, this is a mandatory procedure.
Another element with a modest lifespan is the oil pump. It is this that is often changed even before a major restoration of the power unit is carried out. Along with this part there is a water pump, which is unbearable and, as practice shows, quickly fails. But there is a way out - installing a repair kit, which is quite cheap.
YaMZ 236 thermal gap adjustment technology
The scheme for adjusting thermal gaps with your own hands is practically no different from a similar operation on other cars. After checking that the axle mounting bolts are securely tightened, the crankshaft is turned clockwise until the intake valve of cylinder 1 is completely closed. Then you need to turn the shaft a third of a turn, and only after this can you measure and adjust the gaps in the first cylinder. To set the gap, use special feelers of the appropriate sizes, and after adjusting the first cylinder, carry out the adjustment in the order of work that we gave above.
After installing the gaps, check the condition of the valve cover gaskets, start the engine and test its operation, first at idle, and then under load. The adjustment operation is carried out as necessary or after repair or dismantling of the cylinder heads.