| ZIL-133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturer | ZIL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years of production | 1975—1999 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assembly | ZIL (Moscow, USSR) ZIL (Moscow, Russia) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Cargo | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other designations | "Kroil" | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Layout | front-engine, rear-wheel drive | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wheel formula | 6 × 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Engine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KamAZ-740.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturer | KamAZ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | diesel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | 10.850 cm3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum power | 210 l. With. (154 kW [209 hp according to GOST 8.417]), at 2600 rpm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maximum torque | 637 Nm, at 1500 - 1800 rpm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Configuration | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinders | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Valves | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Environmental standards | EURO-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder diameter | 120 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Piston stroke | 120 mm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compression ratio | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Supply system | diesel | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cooling | liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder block material | Cast iron | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder head material | Cast iron | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resource | 400 thousand km. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Clock (number of clock cycles) | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cylinder operating order | 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recommended fuel | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Type | mechanical |
| Number of steps | 5 |
| Gear ratios | |
| main gear | 6,33 |
| 1st gear | 7,44 |
| 2nd gear | 4,10 |
| 3rd gear | 2,29 |
| 4th gear | 1,47 |
| 5th gear | 1,00 |
| Reverse gear | 7,09 |
| Synchronizers | 2 - 5 gears |
| Switching | floor lever |
| manual 5-speed | |
| Manufacturer | KamAZ |
| Model | KamAZ-14 |
| Type | mechanical |
| Number of steps | 5 |
| Gear ratios | |
| main gear | 6,83 |
| 1st gear | 7,82 |
| 2nd gear | 4,03 |
| 3rd gear | 2,50 |
| 4th gear | 1,53 |
| 5th gear | 1,00 |
| Reverse gear | 7,38 |
| Synchronizers | 2 - 5 gears |
| Switching | floor lever |
ZIL-6309 →Media files on Wikimedia Commons
ZIL-133
- Soviet and Russian truck produced by ZIL. It was mass-produced from 1975 to 1999. The first prototypes were released in 1970. It was a three-axle (6 × 4) national economic modification with increased payload capacity based on the mass-produced two-axle (4 × 2) ZIL-130 truck.
History[ | ]
The development of a higher load-carrying vehicle (8 tons) with a 6 × 4 wheel arrangement based on the 5-ton ZIL-130 began in the first half of the 1960s. The new family was supposed to receive the index 133. The first prototypes were ready in the mid-1960s, but the deployment of their mass production was constantly postponed. The need to produce such a family of trucks was called into question in connection with the planned commissioning of the new Kama Automobile Plant, which was supposed to produce trucks of a similar tonnage class, but of a much more modern design, in particular, with a diesel engine and a “cab-over-engine” layout [ source not 705 days specified
]. Moreover, prototypes of trucks for the future plant were created at ZIL itself (ZIL-170).
However, in 1975, it was decided to begin production of the first model of the three-axle ZIL-133G1 family, which received a long wheelbase, hence the letter “G” in the index. ZIL-133 became the largest carburetor truck in the USSR.[1] Having undergone modernization in 1979, the model received the ZIL-133G2 index, while the load capacity was increased from 8 to 10 tons. Separately, it should be mentioned that the ZIL-133G1 and G2 modifications differ from each other by the outwardly different design of the cockpit hood in the style of the ZIL-130, produced before 1977-78 and after 1978. In fact, the change in cabin design was a stream at the plant and affected the entire model range at once, including the 133 family. Thus, the 133G1 modification, released before the end of 1978, had the old design, and those produced from the end of 1978 had a new design. Modification 133G2 had only a new design, since it had been produced since 1980. The production of these cars was in small series. Back in the mid-1970s, a project was developed for a three-axle ZIL with a KamAZ-740 diesel engine. This model received the index ZIL-133GYA and its production began in 1979. Cars of this modification are easily recognizable by their long hood with an original false grille in the shape of large horizontal bars. The hood had to be lengthened so that the much larger KamAZ-740 diesel engine could fit into its space.[2]
Gasoline ZIL-133G2 were discontinued already in 1983 due to the fact that the diesel version of the ZIL was more efficient - fuel consumption per 100 km at a speed of 60 km/h is 26.6 liters (diesel fuel) for the ZIL-133GYA versus 48 .3 liters for ZIL-133G2 (gasoline).[3]. At the same time, “GY”, being actually a “hood” alternative to the new KamAZs, were already produced in large series, mainly as bare chassis for various installations and less often as on-board ones. Production of the ZIL-133GYA was carried out until 1992 (possibly until 1994 [4]), after which this model was modernized, in particular, it received a cabin from the new family of ZIL-4331 trucks, index 133G40, and was produced at ZIL until 1999.
ZIL-3906 + Photos
17.12.08
The range of multifunctional SUVs of the ZIL-3906 model is capable of operating in very rough terrain. High cross-country ability of vehicles is ensured by all-wheel drive on all wheels with diagonal tube tires measuring 14.00-20″ (370-508) model OI-25 or diagonal tubeless tires measuring 16.00-20″ model IYA-333, their independent torsion bar suspension, the ability to adjust the air in the tires from 0.5 to 3.2 kg/cm, wheel steering on both axles, impressive ground clearance, as well as small front and rear overhangs. Transmission - mechanical. The design of the car includes four final drives (gear ratio 2.09) and four wheel gearboxes (gear ratio 4.27). Clutch and gearbox type ZIL-5301. The transfer case is a two-stage one with an inter-sided lockable differential. The SUV has six power take-off points. The steering is power-assisted for the front and rear wheels. Brakes - four brake systems with disc brakes on final drives. The cars are equipped with a preheater, an insulated hood, and seat belts. In January 2002, production of a new series of off-road vehicles GVA-3848 was launched. Their main difference from the ZIL-3909 is the seven-seat four-door cab from the ZIL-5301GA truck. The GVA-384851 chassis has a base of 4800 mm, GVA-384852 - 4300 mm, GVA-384853 - 3800 mm.
Source: https://legion.wplus.net include"inc_foot.php"; ?> | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
offroad38.ru
Modifications[ | ]
ZIL-133G40, produced in the 1990s
- ZIL-133 - a basic chassis with a medium base with a ZIL-133 carburetor engine. Not serially produced
- ZIL-133B is a short-wheelbase dump truck chassis. Not serially produced
- ZIL-133V - truck tractor. Small-scale production
- ZIL-133G - further development of the ZIL-133 with an extended base (one gas tank and a platform with two side walls)
- ZIL-133G1 - a unified modification of the ZIL-133G (two gas tanks and three side walls) with a lifting capacity of 8 tons. For the purpose of maximum unification with the already produced ZIL-130 family, the gasoline engine with all systems and equipment, a single-disc clutch, and a 5-speed gearbox were unified , as well as all the main components and parts of the steering, parking and service brakes, driveshafts with hinges and splined joints, frame and front suspension parts, elements of the pneumatic system, electrical equipment system, contact-transistor ignition system, cabin with equipment and tail, and with ZIL-131 - front suspension shock absorbers. Serial production 1975-1980.
- ZIL-133G2 - in 1977, a 10-ton model ZIL-133G2 with a total weight of 17.2 tons was added. They were equipped with a standard 150-horsepower V8 gasoline engine, a 5-speed gearbox, a hypoid final drive and a balanced rear wheel suspension on semi-elliptical springs. Serial production 1977-1979.
- ZIL-133D - short-wheelbase dump truck chassis
- ZIL-133D1 - simplified modification of ZIL-133D
- ZIL-144N - agricultural version with rear single-pitch arched tires
- ZIL-133GYA - diesel modification of ZIL-133G2 with KamAZ-740 engine (1979-1992)
- ZIL-133VYA - truck tractor and short-wheelbase dump truck with a KamAZ-740 diesel engine (1979-1992)
- ZIL-E133VYAT is a truck tractor with a KamAZ-7403 engine (260 hp) with turbocharging. Not serially produced
- ZIL-133G40 - further development of the ZIL-133GYA with a 4331 family cab and ZIL-6454 / ZIL-645 / Cat 3116 diesel engines (1992-1999)
- ZIL-133G42 - crane chassis with a cabin of the 4331 family and a ZIL-6454 engine (1992-1999)
- ZIL-133D42 - dump truck chassis with 4331 family cab and ZIL-645 engine (1992-1999)
- ZIL-13305A - truck tractor with extended cab of the 4331 family and ZIL-6454 engine (1993-1999)
- ZIL-133G2A* - modification of ZIL-133G2 with a 4331 family cab and ZIL-508.10 carburetor engine (1993-1995)
- ZIL-133G2B* - chassis with cab of the 4331 family and carburetor engine ZIL-508.10 (1993-1995)
- ZIL-133D52* - dump truck chassis with cab of the 4331 family and ZIL-508.10 engine (1993-1995)
- ZIL-451400 - dump truck with NefAZ body (1997-1999)
- ZIL-630900 - further development of the ZIL-133G40 with the YaMZ-236A engine (1999-2002)
- ZIL-640900 - truck tractor with YaMZ-236A engine (1999-2002)
- ZIL-6309N0 - further development of the ZIL-630900 with the YaMZ-236NE2 engine (Euro-2) (2002-2005)
- ZIL-6309N2 - crane chassis with YaMZ-236NE2 engine (Euro-2) (2002-2005)
- ZIL-45222 - dump truck chassis with YaMZ-236NE2 engine (2002-2005). MMZ body
- ZIL-630980 - modification of ZIL-6309N0 with ZIL-433180 cab with MMZ D-260.E3 engine (Euro-3) (2008). Not mass produced
* Release of carburetor modifications 133G2A, 133G2B and 133D52 in 1993-1995. was caused by the cessation of supplies of KamAZ-740 diesel engines due to a fire at the KAMAZ engine plant.
Family history[ | ]
1990s[ | ]
As a result of the transition of the Russian economy to a market economy in the early 1990s, the main products of AMO ZIL - medium-tonnage gasoline trucks - fell under a landslide reduction in demand, therefore, at the beginning of 1992, the company urgently launched a project to create a three-ton delivery truck with maximum use of already manufactured components from heavier trucks, in particular type 4331 cabs and type 130 gearboxes. The Mercedes-Benz T2 was taken as a prototype for the chassis. The first two running samples of the three-ton ZIL-5301 were manufactured at the end of 1994, and in 1995 a pilot batch of 219 vehicles was produced on a Mercedes chassis (cabin with high headlights). Mass production of the ZIL-5301 series, which received its own name “Bychok” (according to unconfirmed data, on the personal initiative of Moscow Mayor Yu. M. Luzhkov), began in 1996 (1348 units). In 1996-1997, a modular design of an all-metal panel van body was developed, which made it possible to create 2-, 3- and 4-section vans with a volume of 10.5 m³ ZIL-5301NS to 20.5 m³ ZIL-5301ES (wheelbase 3245-4505 mm ). The base model of the van was the 3-section ZIL-5301SS with a volume of 15.5 m³.
The low loading height of the vans (765 mm), small turning radius and the presence of a sliding side door of the cargo compartment (versions without side doors were also produced on request) made it possible to create on their basis cargo-passenger versions with a 6-seater (including the driver) cabin and reduced cargo compartments: 5.5 m³ on ZIL-5301A3; 10.5 m³ on ZIL-5301A2 and 15.5 m³ on ZIL-5301A1 with a removable and collapsible partition between the cabin and the cargo compartment. Commissioned by Mosvodokanal in 2004-2005. 15 ZIL-5301A2 vans were manufactured.
In 1998, based on vans, the ZIL-3250 family of small buses was created, including 15- and 19-seat modifications (base, respectively, 3650 and 4505 mm). The buses received stabilizers for both suspensions and ABS. The Bychok family of buses also included a ZIL-32502M ambulance with a single-pitch tire and air suspension on the rear axle and a ZIL-325SHA staff bus.
2000s[ | ]
By 2000, the share of Bychka in the total production of AMO ZIL reached 56%, which amounted to 12.3 thousand vehicles. Thus, this family was able to provide the plant with the necessary capacity utilization. In the second half of the 2000s, due to the deterioration of the enterprise’s financial performance and increased competition from domestic analogues (GAZ-3310 Valdai) and foreign (primarily Korean and Chinese) brands, Bychka’s share in production began to rapidly fall. In the mid-2000s, it was planned to organize the assembly of improved “Bulls” for the markets of Eastern Europe at the AMO Plant in Jelgava, Latvia [ source not specified 976 days
]. Such a car was supposed to receive a different design for the front part of the body, a new interior, a Cummins diesel engine, a ZF gearbox, disc brakes, and the model’s load capacity was supposed to be increased to 4.5 tons. As a result, the project was never implemented. In 2008, the share of Bychka in the total (significantly reduced) production of AMO ZIL accounted for only 11.6% (527 units). The production of a family of vans and buses has actually been reduced to single orders. Low build quality and the lack of a suitable diesel engine reduced the popularity of the “Bychok” series even among federal and metropolitan municipal structures that traditionally purchased AMO ZIL products. From the mid-1990s to 2006, on the basis of the Bychka, a reinforced 4.5-ton ZIL-4362 family was developed, the mass production of which, however, was constantly planned to be part of the Tapir family. However, the launch of the modernized Tapir family (4.5-6 tons of payload capacity), scheduled for 2008, was constantly postponed, which also did not strengthen the competitive position of AMO ZIL.
Until 2005, the ZIL-5301 was equipped with diesel engines MMZ D-245.12S and MMZ D-245.9 (both Euro-0). In January 2005, the entire Bychkov family received MMZ D-245.9 E2 (Euro-2) diesel engines, and since April 2008 - MMZ D-245.9 E3 (Euro-3). Modifications with modernized engines received different factory indices (see Modifications).
2010s[ | ]
On December 26, 2011, the ceremonial launch of the assembly line for ZIL-5301 vehicles (ZIL “Bychok”) took place at the Petrovsky Auto Parts Plant AMO ZIL CJSC (Saratov Region, Petrovsk). The production of ZIL-5301 vehicles was moved from Moscow from the head site of AMO ZIL[1]. However, already in 2014, production of the car was finally completed[2].
Special vehicles[ | ]
ATs-40(133G2)-181 KS-3575A
- KSA-7 is a prototype spreader with a lifting capacity of 7 tons based on the ZIL-133G1. Arched tires were installed on the rear axles.
- Truck crane KS-3575A
- Fire tank trucks AC-40(133G2)-181, AC-40(133GYA)-181A
- Fire ladder AL-45(133GYA)PM-501
- Combined extinguishing vehicle AKT-2.5/3(133ГЯ)-197
- Concrete mixer SB-159B1
- Loader of machines for applying mineral fertilizers ZMU-8
- Automotive seeder loader ZSA-7
- Tank truck with a pneumatic unloading system and a useful volume of 15 m3 ASP-15
- Articulated lift AGP-28
- Combined road vehicle ED-403
- Van for transporting horses KAvZ-59821[6]
- Cash collection vehicle DISA-6938
ZIL-390610 Photo Characteristics Load capacity Weight
ZIL-390610, all-wheel drive off-road cargo vehicle. Designed for transportation of various cargoes and equipment on roads and in off-road conditions. The first copy rolled off the ZIL assembly line in 1996. The model was developed similar to the multi-purpose German SUV Unimog.
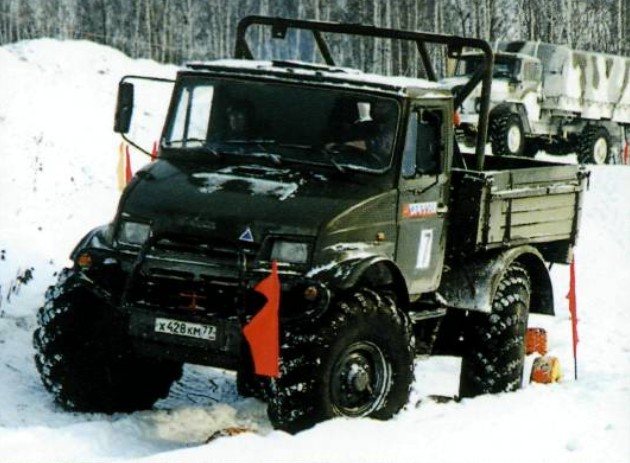

High cross-country ability is achieved thanks to all-wheel drive, independent torsion bar suspension for all wheels, steering of the wheels of both axles, the ability to adjust the air in the tires, as well as a short wheelbase and small front and rear overhangs. A basic model and modifications are produced, differing in wheelbase size: ZIL 390611, ZIL-390612, ZIL-390613, ZIL-390614, ZIL-390616.

The car has a 4x4 wheel arrangement and is equipped with a four-cylinder diesel engine MMZ D 245.12 with a displacement of 4.75 liters and a power of 105 hp. With. The ZIL 3906 design includes four final drives and four wheel drives. The truck is equipped with a mechanical onboard transmission, a five-speed gearbox, power steering, preheater, and seat belts.
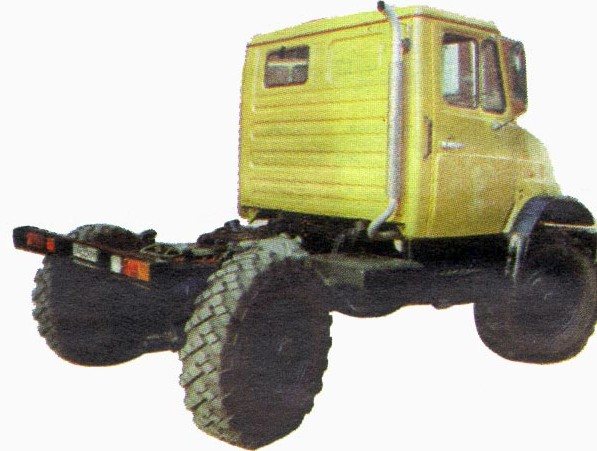

The SUV's carrying capacity is 3250-3200 kg, maximum speed is 80 km/h. 19 liters of fuel are consumed per 100 km at a speed of 60 km/h. In December 1996, at the first truck trial competition, the AMO ZIL team, which competed in a car, took first place. In February 1998, ZIL 390610 again became the winner of the second truck trial competition. In October 1999, at the 1st Open Cup of Belarus in truck trial, ZIL 390613 took seventh place.

In the gaming and souvenir industry[ | ]
Since 2014, the ZIL-133GYA model in 1:43 scale is available from Start Scale Models, from 2020 - from Avtoistoriya, and from 2020 (with traces of use) - from ModelPro.
On October 25, 2014, a 1:43 scale model of the KaVZ-5982 (ZIL-133G1 chassis) was released as part of the “Vehicle in Service” project (No. 78, “Transportation of Horses”).
In 2020, Start Scale Models released models of the KS-3575A (133GYA) and ATs-40 (133GYA) truck cranes.
In 2020, the ZSA-7 (133GYA) model was released from ModelPro.
In 2020, ModelPro released the following models: ZMU-8 (133GYA), ASP-15 (133GYA) and AKT-3/2.5 (133GYA).
Specifications
The wheel formula of the car is 6x6. The front axle is switchable. The middle axle is intermediate, through which power is supplied to the rear axle. All bridges are blockable. The transfer case has a hatch for power take-off (up to 60 hp) for additional equipment of special equipment. The gearbox is mechanical, five-speed, the transfer case is two-speed, the frame spars are 8 mm thick.
The steering mechanism is equipped with a hydraulic booster. The turning radius is 10 m. The car overcomes a rise at an angle of 35° and a ford with a level of up to 1.4 m. Ground clearance is 33 cm.
The suspension of all wheels is dependent (spring with hydraulic shock absorbers in front, spring-balanced on the second and third axles). Drum brakes. The brake system is pneumatic, single-circuit, with the ability to connect a trailer. Tire pressure is adjustable, and it is possible to pump up a punctured tire while driving. The voltage in the on-board network is 24V, there are two batteries.
Load capacity
For model 4334B1:
- Load capacity: 3750 kg
- Gross weight: 11170 kg (with winch)
- Curb weight: 6955 kg
- Towed trailer weight: 4200 kg
- Permissible total weight of the road train: 15370 kg
- Loading platform dimensions: 3810 mm x 2420 mm x 600 mm
- Turning radius: 10.2 m
- Maximum speed: 90 km/h
Notes[ | ]
- Eight-ton three-axle ZIL - Behind the wheel, 1976, No. 8
- ZIL diesel trucks - Behind the wheel, 1979, No. 11
- Brief automobile reference book NIIAT. Tenth edition, revised and expanded - M., Transport, 1985
- 700 thousand rubles for the Soviet truck “Baba Yaga” // Article dated May 21, 2019, “Mail.ru”.
- Glukhovsky D. M., Melamud R. A., Mitrofanov V.
P. Cars of the ZIL-133 family. - M.: Transport, 1984. - 328 p. - KAvZ in chronological order