Those who were born in the USSR in the 50-70s of the last century remember very well the long yellow Hungarian buses of the Ikarus brand, which, bending bizarrely, overcame sharp turns, since they constantly traveled on them, paying 5 kopecks for travel (some I also traveled for free - as a “hare”).
This is how the division of labor worked within the world system of socialism. Hungary supplied Ikarus buses to all countries that are members of the CMEA (Council for Mutual Economic Assistance), as well as to many African countries and individual European countries (Sweden, West Germany, Finland and a number of others). It is interesting that, as a rule, buses of the same model were delivered to different countries in different “colors”. Later, when the Ikarus brand (more correctly pronounced “Ikarush” with the accent on the first syllable) became known throughout the world, joint ventures were organized in the developed industrial countries of North America, as well as in Cuba, North Korea and Indonesia.
History of the brand
And it all began at the very end of the century before last with a small workshop in Budapest (Austria-Hungary), which was founded by Imre Uri. After 30 years, this company began producing bus bodies, and under his sons, 1,000 buses were assembled in 1939.
After the end of World War II, the company was nationalized and, merging with JSC Ikarus, retained the name of the latter. This company began its path to world fame in 1962 after the transfer of the plant in Székesfehérvár to it. This plant was specially built for the production of Ikarus buses of the 200th model. The overwhelming majority of city and intercity buses were supplied to the Soviet Union. With its collapse, the company, naturally, having lost its sales markets, curtailed almost all of its production and was divided into two - according to the number of factories (Budapest and Székesfehérvár), which carried out individual orders.
In the penultimate year of the last century, the Ikarusbus group tried to breathe “life” into them, but failed. In 2007, the EAG company (plant in Budapest) was officially declared bankrupt, and in Szekesfehérvár, surviving “from bread to kvass”, exists today in conditions of fierce competition within the European Union.
Body
Assembled from square pipes, carriage type. The designers envisaged a service life of at least three decades. Unfortunately, such a design entails unpleasant consequences. If the bus was operated in difficult climatic conditions without major repairs, then the sections of the body in its rear part literally sagged, severely deforming the interior. On the sides there are two large luggage compartments (one on each side), each with a volume of 5.3 m3. There are two ways to open the compartments: either using a hand lever directly on the body, or using a button on the dashboard.
The rear bumper on the Ikarus 250 bus (you will see the photo in this material) is metal, attached to the body using welded fasteners. The first buses in the series had almost exactly the same bumper installed on the front, differing in some minor details. Due to the practical structural uselessness of metal, plastic structures were subsequently installed, which made it possible to somewhat reduce the cost of the structure.
"Ikarus" up to 250 model
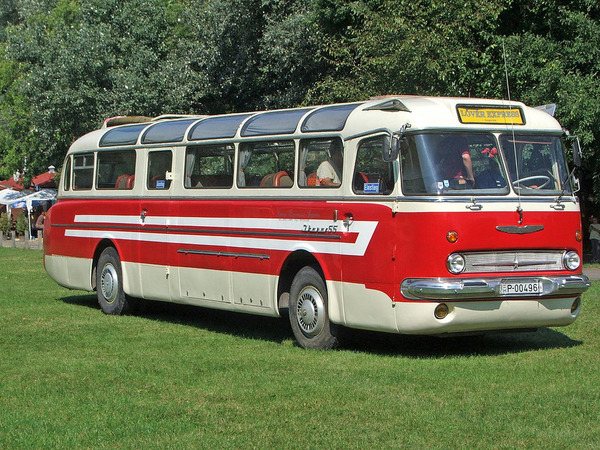
In 1953, production of intercity buses model 55 with a carriage-type body began, and a year later the Ikarus-Lux.
These were very comfortable buses for those years and were produced (with minor improvements) for two decades. Drivers called the Ikarus-Lux a “vacuum cleaner” for its futuristic (cigar-like profile, square face), headlight above the windshield and noisy engine. 11 meters long, it had a six-cylinder diesel engine with 170 hp, which was located at the rear. This ensured that there was no corresponding smell in the cabin, which was common when subsequent models of this brand were used in Russia. Thirty-two soft seats, a suspension with hydraulic shock absorbers and a top speed of 98 km/h provided comfortable travel conditions. These buses were very reliable and lasted up to a million kilometers without major repairs.
In 1966, the production of the super-capacity, more than 16 meters long (there were countless people jammed there) city bus “Ikarus” model 180 began, which lasted seven years. It was white with a red stripe, with a carriage-type body that had four passenger doors and an accordion vestibule, as well as body regulators powered by compressed air. The engine is also a six-cylinder diesel, 192-horsepower Raba-MAN. The maximum speed (63 km/h) in urban conditions was almost impossible to achieve. There was little comfort in this model, for which in the USSR it was nicknamed “cattle carrier”, and for its appearance it was also called “accordion”. This model was replaced in the 70s of the 20th century by the Ikarus-280.
External parameters
External characteristics of transport play an important role when choosing equipment. This is due to the tasks assigned to the future owner. Also, the external parameters of the equipment affect other important characteristics, in particular, capacity and weight.
How many seats are there in the cabin?
The Hungarian manufacturer focuses on producing high-capacity models that are used on long-distance routes and can comfortably transport about 40-50 people. Particularly large examples with an articulated body were previously widely represented in the manufacturer’s lineup. They are intended mainly for urban conditions. The ability to accommodate 170-180 passengers and seat 20-30 people are characteristics of the Ikarus, which ensured their successful use on routes in large cities with significant passenger traffic .

Intercity bus Ikarus 55. Photo Wikipedia
Medium-capacity models are not actively represented in the assortment. The company's first developments belonged to this capacity class: intercity and suburban Ikarus, 60 and , the number of seats in which was 31+1, 23/27 and 32, respectively. Small-capacity models have not been very popular for a long time, so buses of this type are practically not found in the company’s assortment. There are no particularly small options at all.
Sizes/dimensions of accordion and other types
Body dimensions directly affect interior capacity. First of all, this concerns the length of the structure, but more on that later. For now, let's look at the width and height of the models . Buses operating on public roads cannot have a body width of more than 2.5 meters. The manufacturer complies with this standard and produces (and previously produced) equipment of any type in accordance with this requirement . For example, Ikarus apron models number 290 and 695 had a body width of 2500 mm.

The height of the equipment differs depending on the number of levels/floors . Standard one-story models have an average height of 3 meters . One-and-a-half-story ones, found in the assortment in small quantities and reminiscent of two-story ones, since the floor of the cabin was located high, and the transport itself with two levels had a height of 3.8 meters . A similar parameter is inherent in the Ikarus 692 model, another unique development that never went into mass production.
Length
According to the size (length) of the bus and capacity, five types are distinguished. As noted earlier, there were only four types in the company’s line. The average for models of different types is 7.5; 10.5; 12 and 17 meters. The body length of the middle class Ikarus allows us to classify them as large vehicles.

Bi-articulated bus Ikarus 293. Photo Wikipedia
But it should be understood that classification criteria have changed over time. In addition, body dimensions often make it possible to classify models as one type, and capacity as another. In addition, the plant’s product range included original solutions, for example, the Ikarus 293 model, which is almost 23 meters long and consists of three passenger sections connected by two articulation units.
Weight
The concept of “weight” usually means the curb and total (technically permissible) weight of the bus. And if the first parameter is only one of the characteristics of the equipment, then the second value significantly influences both the choice and operating conditions . Exceeding the indicator (vehicle overload) can lead to a malfunction, an emergency situation on the road, injury to passengers, the driver, etc.

City bus Ikarus 260. Photo Wikipedia
Therefore, the weight of the model is always indicated in the technical specifications. For buses of the Hungarian manufacturer, the weight of the equipped vehicle is approximately 13 tons, the average gross weight is about 20. The parameters of the popular Ikarus 260 model are 9000 and 16000 kg. respectively.
Driver's cabin
Depending on the model, the driver’s workplace may have a different appearance:
- with and without partition;
- with and without a separate door;
- with a mechanical or pneumatic door.

City bus Ikarus 280. Photo Wikipedia
But regardless of the type and model of the bus, it is possible to note the competent design of the cabin. The designers constantly worked to make the driver's seat spacious, comfortable, safe , and they succeeded. A comfortable adjustable (for intercity/tourist models) seat, space for the driver’s personal belongings, excellent visibility – these are the components that ensure high-quality performance of duties without fatigue for a long time. The driver's cabin of some models, for example, Ikarus 280, even now looks quite modern, meets standards and requirements.
Dashboard
The instrument panel is informative and the switches are convenient. The panel is “at hand”; the driver does not need to reach for the instruments. In most models of previous years, the panel is divided into several zones , which also contributes to driver convenience.
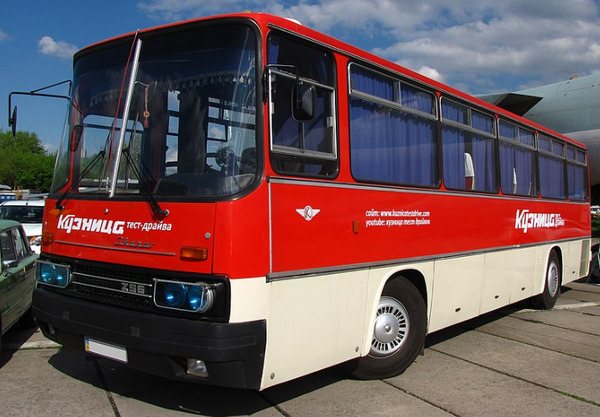

Bus Ikarus 256. Photo Wikipedia
This was the case on the popular Ikarus 256 bus. There were three zones. On the left side there were buttons for controlling lighting and windshield wipers, starting the engine, a central switch with a key and a tachometer. On the central part there were pressure gauges for the pneumatic system, a speedometer, a “ground” button and an “electrical combined” instrument that combines indicators for fuel level, coolant temperature and engine oil pressure, a voltmeter, indicator lamps for direction indicators, battery charging and a pressure drop alarm. oils The right zone contained buttons for opening/closing doors, stopping the engine, as well as those responsible for the operation of the audio system, driver and tour guide microphones. Modern models are equipped with a color LCD display, which displays the most important indicators of the machine.
Colors: green, blue and more
Buses come off the plant's conveyor belt, the body of which is made in various colors . The designs of modern vehicles are painted either in bright colors: red, blue, green, or have a white body color. Two- and three-color buses are rare. While previous years' models were mostly painted in more than one color .
Vehicles with a white body and a longitudinal stripe of a different color were common: blue, red, green, the location of which was different. The buses had a non-standard design, the body of which was painted in bright colors: yellow, blue, red, and the doors were white.
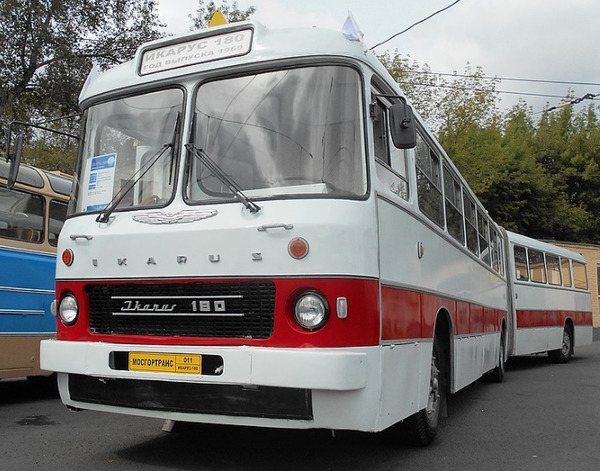

City articulated bus Ikarus 180. Photo Wikipedia
The manufacturer produced models adapted to certain operating conditions for different countries. Adaptation involves adapting not only technical characteristics, but also decorative ones, including body paint. For example, Ikarus 556 and 180 buses supplied to the USSR were painted white with a longitudinal dark red or dark blue stripe.
Magnificent "wanderer" - "Ikarus-256"
The Ikarus-256 model was produced for half a century, which first came off the assembly line in 1977. It was a slightly improved Ikarus-250 - more comfortable and a meter shorter (length 11 meters). The capacity of the Ikarus bus was designed to transport tourists, including foreign ones, and it had 45 soft seats. The last five seats are combined into a “sleeping” sofa, which is slightly raised (two steps) above the rest of the bus interior. An undoubted innovation for that time was the presence of a TV mounted to the right of the driver. In contrast to all this splendor were the luggage racks that this model inherited from the Ikarus-255 (fabric mesh on the frame).

The design remained unchanged. The body is monocoque, carriage type, the engine is rear-mounted and more powerful than on previous models (250 l/s). The luggage compartment has become significantly larger. The location of the company logo and the number 256 is above the air intake. There was a panoramic, two-part, huge windshield, rear-view mirrors of the “hare ears” type and powerful two pairs of headlights with lens coating.
Convenience/inconvenience for passengers
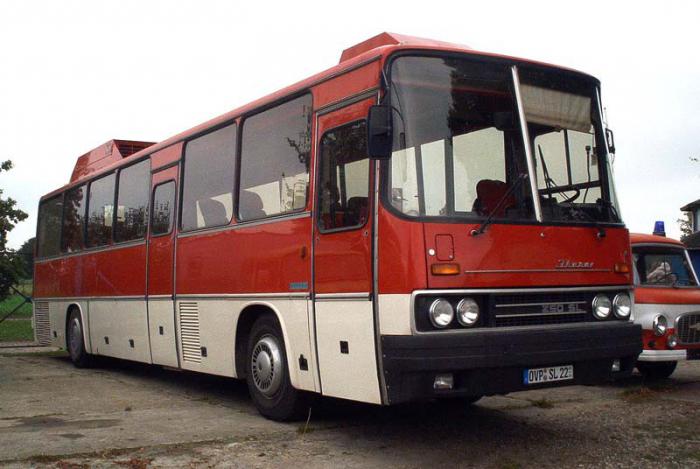

Three lampshades with eight lamps each provide general lighting for the interior. Heating – radiators installed under each pair of seats; the engine cooling system is responsible for heating the liquid. The bus is notable for the fact that its floor is significantly lower than the level of the seats. This not only made it possible to significantly expand the luggage compartment, but also completely isolate the “bulges” from the wheels. However, it is the design of the cabin that makes the Ikarus 250/40 (and its other varieties) practically unsuitable for city use, since passengers who often have to get in and out find it extremely uncomfortable in a narrow aisle.

In normal configurations, blinds were mounted on the windows, which were very convenient on long flights during the day, when the sun could prevent people from taking a nap. The front part of the cabin is distinguished by the presence of an additional folding seat, which is used by guides, controllers, or an additional driver sits there. In the export versions of the Ikarus 250/40 (photos of the bus are presented in the article), a special room with a toilet and a small refrigerator was installed at the end of the building. Unfortunately, in the European part of the USSR this variety was no more common than some kind of Cadillac. Additional five seats were placed in the rear of the cabin, although it was extremely bad to ride in them due to the strong vibration of the engine and the heat from it.
Model 260
For a third of a century, until the second year of our century, the production of the Ikarus-260 bus continued. Interestingly, this model had 30 modifications (versions were even produced for mountainous regions). Unlike other buses of this company, the color of the Ikarus delivered to the USSR was yellow.

Also, for the first time, air suspension was used, which was previously mechanical and “burned out” after a year of driving. The body is standard, with three passenger doors (four folding doors). The engine is located under the floor, the cabin is heated both from the engine cooling system and by air. Capacity up to 107 people, seating – 22. At full capacity, the weight of the bus could exceed 15 tons. The maximum speed of 66 km/h was not allowed within populated areas.

Specifications
Are common
- Body type - monocoque
- Number of seats (“Lux”) – 32 (34)
- Number of doors (“Lux”) – 2 + driver’s (1 + driver’s)
- Fuel capacity, l - 250
- Weight, kg:
dry — 9,300 equipped — 9,500 full — 12,730
- Total weight distribution, kg:
on the front axle - 4,250 on the rear axle - 8,480
- Turning radius along the front outer wheel track, m - 10.25
- Maximum speed with full load, km/h - 98
- Maximum climbability, % - 27
- Control fuel consumption, l/100 km - 32
- Trunk capacity, m³ – 4.8
- Dimensions, mm:
length - 11,400 width - 2,500 height - 2,870
- Wheelbase, mm - 5,550
- Ground clearance, mm - 290
- Overhangs, mm:
front - 2,300 rear - 3,385 [ source not specified 78 days
]
Engine
- Location - rear
- Model - “Csepel D-614”
- Type - four-stroke, diesel, pre-chamber
- Number of cylinders - 6
- Number of crankshaft supports - 7
- Cylinder arrangement - in-line
- Valve location - top
- Cylinder diameter, mm - 112
- Piston stroke, mm - 140
- Cylinder displacement, l — 8.28
- Compression ratio - 19
- The operating order of the cylinders is 1-5-3-6-2-4
- Maximum power (“Lux”), l. With. — 145 (170) at 2300 rpm
- Maximum torque, kg m - 50 at 1400 rpm
- Minimum specific fuel consumption, g/l. s.ch - 190
- Cooling system - liquid
- Lubrication system - combined
- Dry engine weight, kg - 630 [ source not specified 78 days
]
Transmission
- Clutch - single disc, dry
- Gearbox - mechanical, five-speed, three-way, with synchronizers for 2nd-5th gears
- Gearbox ratios - I-6.17; II-2.99; III-1.59; IV-1.00; V-0.78; Z.H.-6.68
- The main gear of the rear axle is two-stage, gear ratio is 5.85
- Gearboxes:
central - bevel, gear ratio - 1.78 wheel - planetary, gear ratio - 3.28 [ source not specified 78 days
]
Steering
- Steering mechanism - globoidal worm and double roller, gear ratio - 29
- Amplifier - hydraulic [ source not specified 78 days
]
Brake systems
- Working - drum type, on all wheels, with pneumatic drive
- Parking - drum type, on rear wheels, with mechanical drive
- Retarder - motor, valve type, closing the engine exhaust pipe and fuel supply, pneumatically controlled [ source not specified 78 days
]
Modular design
The Ikarus-280 bus replaced the Ikarus-180, which had already exhausted its service life. The main idea of this model was its modular design, so it had more than fifty modifications. It was possible to change everything in it - from the length of the bus itself (maximum 18 meters), the number of doors (from one to four) to almost any brand of engine and type of transmission.

In outline it was already a regular parallelepiped with a rounded frontal view. The engine produced 190 l/s, was located under the floor, and had a service life of half a million kilometers before major repairs. Large areas accommodated more than one and a half hundred passengers, with 35 seats. The floor was covered with a rubber carpet. Smooth running (a distinctive feature of the Ikarus-280) was achieved by a large number of air cylinders. The drum brakes are equipped with a pneumatic drive.
What technical characteristics does the Ikarus bus have:
What does the Ikarus bus look like? The reader can see his photo in our article.
Differences in the parameters of models for different purposes
| Options | Tourist | Intercity | Urban | Suburban |
| Purpose | To cover long distances while ensuring comfort for passengers | To cover medium and long distances while ensuring comfort for passengers | For driving within the city on roads with high-quality, smooth surfaces | For covering short and medium distances on roads with imperfect surfaces |
| Floor location | High-floor | High-floor | In most cases low-floor | High-floor |
| Interior layout | Luggage compartments. A large number of seats, and, accordingly, narrow passages. Comfortable seats. | Luggage compartments. A large number of seats, and, accordingly, narrow passages. Comfortable seats. | Significant capacity is facilitated by the relatively small number of passenger seats and large storage areas. Wide aisles. Large doors. Convenient handrails. | Plenty of seating. Ability to develop significant speed. |
| dimensions | Mostly big | Mostly big | Mostly large and extra large | Mostly big |
| Peculiarities | Interesting design, the use of new solutions for specific periods of time, comfort, an extensive list of modifications, the creation of machines adapted for certain operating conditions | Interesting design, the use of new solutions for specific periods of time, comfort, an extensive list of modifications, the creation of machines adapted for certain operating conditions | Significant capacity, application of the latest solutions and technologies | Development and implementation of new effective solutions, comfort for passengers and convenience for the driver |
Delivery of Ikarus to the USSR and post-Soviet space
As mentioned above, almost all Ikaruses were sent for operation in the USSR. Firstly, to pay off oil and gas supplies, and secondly, it was taken into account that in the 70s of the last century its population exceeded a quarter of a billion people. The peak of deliveries occurred at the end of the 80s of the 20th century, and in total in the second half of this century (including deliveries to the renewed Russia), more than 140 thousand copies of various models and modifications arrived to us. In addition, in the “dashing” nineties, the Ikarus bus was assembled in Moscow, Kurgan and Arzamas. The last batch was delivered to the Republic of Tajikistan in 2002.
"Ikarus" - an accordion, especially under operating conditions in the USSR, had the following negative effect. Some of the equipment was located under the floor of the passenger compartment, and after frequent repairs, which were carried out by Soviet rather than careful Western specialists, the seals no longer prevented the penetration of soot and exhaust gases into the cabin, for which the buses began to be popularly called “gas chambers.”
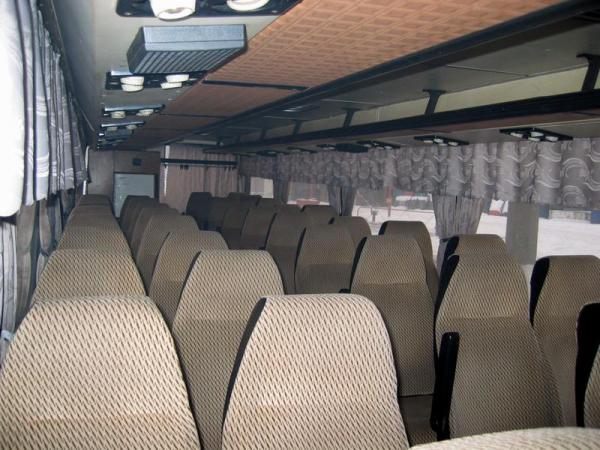

This year marks the half-century anniversary of the start of deliveries of the Ikarus-256 bus to Moscow. Mosgortrans has a bus of this model that is still working. He is registered in Novokosino, where the fourth park is located. He has already covered 700 thousand km. (seven stars on board) and continues to work smoothly. Another such specimen works in the working village of Sapozhok, Ryazan region.
About the manufacturer, production features
Founded in 1895 as a forging and carriage workshop, the company was actively developing, creating new solutions for comfortable and safe passenger transportation. The company's specialists developed and produced vehicles that meet current standards. In addition, the plant employees focused on developing non-standard vehicles for that time. The manufacturer was the first to propose many now common solutions : a bus with a monocoque body, modular design technology.
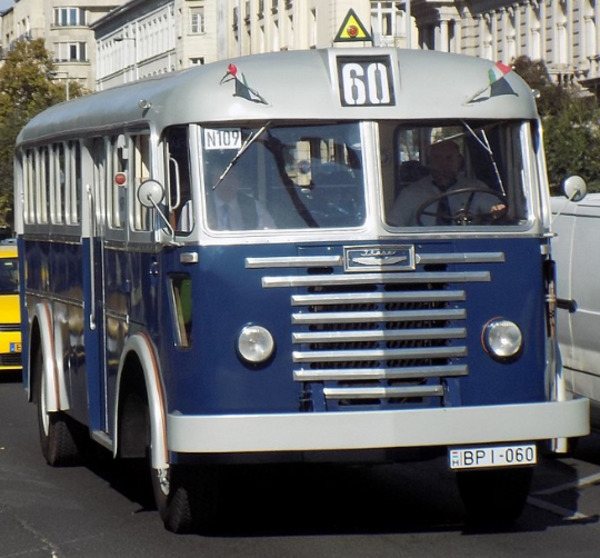

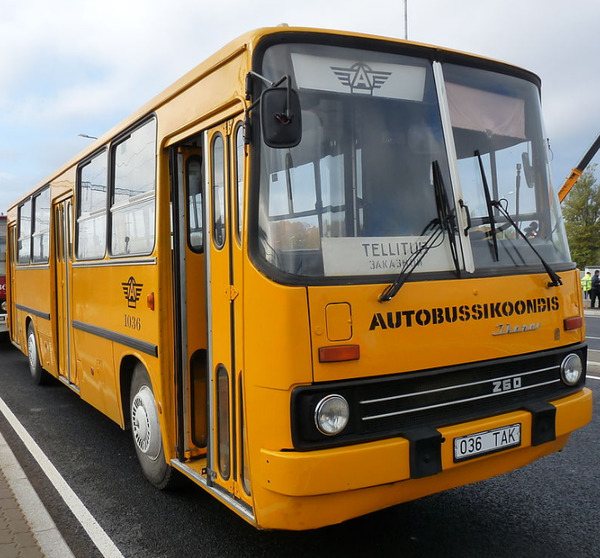
Bus Ikarus 60. Photo Wikipedia
Using high-quality and reliable components, testing finished models, making (if necessary) changes for modernization - all this allows us to offer customers equipment with a wide range of advantages . The main positive characteristics are:
- long service life, which can be verified by seeing operating machines that were produced 20-30 years ago;
- reliability;
- unpretentious operation;
- competent interior layout, optimal for each individual type of model.

Suburban/intercity bus Ikarus 66. Photo Wikipedia
Despite the continuation of activities in the production of passenger vehicles, the article focuses on models of past years . Since the heyday of the enterprise occurred in the second half of the 20th century. However, do not forget that the operating principles have been preserved, the company continues to offer reliable, safe, comfortable vehicles that meet the latest standards, they will also be mentioned in the article.
For reference, it is worth noting that some sources call “modern” buses vehicles produced several years before the dissolution of the enterprise in 2003. While in this article, “modern” refers to those vehicles that are presented for sale on the site as of 2020.